Introduction
The nursing care market has become a cornerstone of the global healthcare ecosystem, addressing the growing demand for comprehensive patient support, long-term care, and specialized nursing services. Nursing care encompasses a wide range of services, including in-home care, hospital-based nursing, elderly care, rehabilitation services, and specialized care for chronic diseases. With the increasing aging population, rising prevalence of chronic illnesses, and advancements in healthcare infrastructure, the demand for quality nursing care is expanding rapidly across the globe.
Furthermore, nursing care plays a pivotal role in ensuring patient safety, improving treatment outcomes, and enhancing the overall quality of life. Nurses are not only caregivers but also educators, advocates, and coordinators who bridge the gap between patients, families, and healthcare providers. This multifaceted role has made nursing care an indispensable component of modern healthcare systems.
In addition, technological advancements, telehealth integration, and innovative care delivery models are transforming the nursing care market, enabling more efficient, personalized, and accessible services. The market encompasses a wide array of stakeholders, including healthcare facilities, home care providers, nursing professionals, training institutions, and policy-makers.
This guest post explores the evolution of the nursing care market, current trends, challenges, market scope, market size, and key factors driving growth, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential healthcare segment.
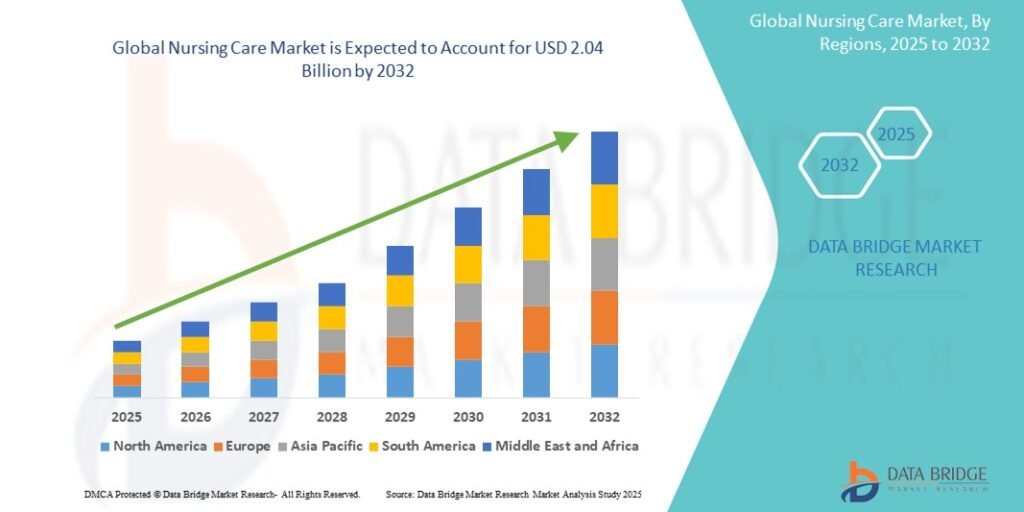
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-nursing-care-market
The Evolution of Nursing Care Market
The nursing care market has evolved significantly over the past century, reflecting broader changes in healthcare, demographics, and societal needs. Historically, nursing care was informal and family-based, with care provided at home by relatives, community members, or religious institutions. However, as healthcare systems advanced, formalized nursing education and professional standards emerged, laying the foundation for modern nursing care services.
The mid-20th century marked the professionalization of nursing, with structured training programs, certification requirements, and the establishment of nursing organizations. Hospitals and healthcare institutions increasingly relied on trained nurses to provide critical patient care, monitor treatment protocols, and manage post-operative recovery.
Subsequently, the rise of chronic diseases, longer life expectancy, and the aging population created a demand for long-term care services, including nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and in-home nursing support. This transition shifted the focus from acute care to continuous, patient-centered care, emphasizing quality of life, rehabilitation, and preventive measures.
Technological innovations, such as electronic health records, telemedicine, and remote patient monitoring, further transformed the nursing care market. Nurses could now coordinate care more effectively, track patient progress in real-time, and provide timely interventions even in remote locations.
Moreover, the emergence of specialized nursing roles—such as geriatric nursing, pediatric nursing, oncology nursing, and palliative care—has expanded the scope of services. These specialized roles address specific patient needs, ensuring comprehensive, targeted, and high-quality care.
The evolution of the nursing care market thus reflects a shift from informal, family-based care to professionalized, technologically enabled, and highly specialized healthcare services that cater to diverse patient populations across the globe.
Market Trends
Several key trends are shaping the nursing care market and driving its global expansion.
Firstly, there is a growing emphasis on home-based and community nursing care. Patients increasingly prefer receiving care in familiar, comfortable settings, leading to the proliferation of in-home nursing services, remote monitoring, and telehealth support. This trend is particularly pronounced among elderly patients, individuals with chronic conditions, and post-operative patients.
Secondly, integration of technology and telemedicine is transforming the nursing care delivery model. Remote monitoring devices, mobile health applications, and teleconsultations enable nurses to track vital signs, manage medications, and provide real-time guidance, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions.
Thirdly, specialization in nursing care is gaining traction. Geriatric nursing, palliative care, wound care, oncology nursing, and pediatric nursing are increasingly recognized for their importance in addressing specific patient populations, creating opportunities for specialized services and training programs.
Moreover, there is a growing focus on preventive and rehabilitative care. Nurses are actively involved in health education, lifestyle counseling, vaccination programs, and post-surgical rehabilitation, which not only improve patient well-being but also reduce healthcare costs and hospital burden.
Another notable trend is the adoption of workforce management and training initiatives. Continuous professional development, certification programs, and skill enhancement courses ensure that nursing professionals remain updated with the latest medical practices, technologies, and care protocols.
Additionally, public-private partnerships and policy support are enhancing the accessibility and affordability of nursing care services. Government initiatives, insurance coverage, and regulatory frameworks are increasingly encouraging private sector participation in long-term care and home nursing services.
Furthermore, the rise in patient-centric care models emphasizes personalized nursing interventions, holistic care, and patient engagement, reflecting a broader shift in healthcare toward value-based and outcome-driven services.
Finally, global aging trends and increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses are fueling demand for continuous nursing care, rehabilitation services, and assisted living solutions, positioning the market for sustained growth over the coming decades.
Challenges in the Market
Despite promising growth prospects, the nursing care market faces several challenges that could impact expansion.
One major challenge is the shortage of skilled nursing professionals. Many regions face insufficient numbers of trained nurses to meet growing demand, which can compromise the quality of care and increase workload stress among existing staff.
Another significant challenge is high operational costs. Providing comprehensive nursing care, particularly home-based or specialized services, involves significant investment in training, technology, and logistics, which can limit market accessibility.
Additionally, regulatory compliance and licensing requirements vary across regions, creating barriers for service providers. Navigating complex healthcare regulations, quality standards, and reimbursement policies can be challenging for new entrants and existing operators alike.
Moreover, limited awareness and cultural perceptions in certain regions may hinder adoption of professional nursing care. In some cultures, family-provided care remains the preferred model, limiting demand for external nursing services.
Furthermore, technology adoption challenges exist in less developed regions. While telehealth and remote monitoring can enhance care, limited digital infrastructure, low technological literacy, and high implementation costs pose barriers.
Lastly, financial constraints among patients may affect access to premium nursing care services, particularly in emerging markets where insurance coverage is limited or out-of-pocket healthcare expenses are high.
Market Scope
The nursing care market encompasses a broad range of services, delivery models, and end-user segments:
-
Services: Home-based nursing care, hospital and clinic-based nursing, elderly and geriatric care, palliative care, rehabilitation services, chronic disease management, pediatric nursing, and specialized clinical nursing services.
-
End Users: Elderly individuals, patients with chronic illnesses, post-operative patients, individuals requiring palliative or hospice care, families seeking in-home care support, hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers.
-
Delivery Models: In-home care services, hospital nursing, outpatient and community care programs, telehealth-enabled nursing, and assisted living facilities.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the market due to established healthcare infrastructure, high awareness levels, and aging populations. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are witnessing rapid growth due to rising healthcare expenditure, urbanization, and increasing awareness of professional nursing services.
The market scope also extends to training, certification programs, and workforce development initiatives, highlighting opportunities for skill enhancement, professional growth, and service quality improvement.
Market Size and Factors Driving Growth
The nursing care market has demonstrated steady growth and is projected to expand further over the next decade. Several factors are driving this momentum:
Firstly, the aging global population is a primary growth driver. Increasing life expectancy and higher prevalence of age-related diseases create sustained demand for elderly care, rehabilitation, and chronic disease management services.
Secondly, rising prevalence of chronic illnesses such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and respiratory disorders fuels demand for long-term nursing care and specialized interventions.
Thirdly, technological integration in healthcare—including telemedicine, remote monitoring, and digital health platforms—enhances service efficiency, patient engagement, and care outcomes, thereby increasing demand.
Moreover, growing awareness about professional nursing care and patient-centric services encourages families to seek external care support, particularly in regions with dual-income households and urban lifestyles.
In addition, expansion of home-based care services provides convenience, comfort, and cost-effective alternatives to hospital care, driving adoption among elderly and post-operative patients.
Furthermore, government initiatives, insurance coverage, and policy support for long-term care, palliative care, and in-home nursing services stimulate market growth by improving accessibility and affordability.
Lastly, training and workforce development programs enhance the availability of skilled nursing professionals, ensuring higher quality care, improved patient satisfaction, and market credibility.
Consequently, a combination of demographic trends, chronic disease prevalence, technological advancements, policy support, and workforce development ensures sustained growth for the nursing care market globally.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the nursing care market represents a vital and rapidly expanding segment of the global healthcare ecosystem. From traditional hospital-based nursing to technologically enabled home care and specialized clinical services, the market has evolved to meet the diverse needs of patients across age groups, health conditions, and geographies.
While challenges such as workforce shortages, high operational costs, regulatory complexities, and technology adoption barriers persist, the opportunities for growth remain substantial. Rising aging populations, increasing chronic disease prevalence, technological innovations, awareness campaigns, and supportive government policies collectively drive market expansion.
Ultimately, the nursing care market is not merely about patient support; it is about improving quality of life, enhancing healthcare outcomes, and delivering personalized, comprehensive, and accessible services. As healthcare systems continue to evolve and demand for professional nursing care increases, the market is poised for sustained growth and long-term global relevance.